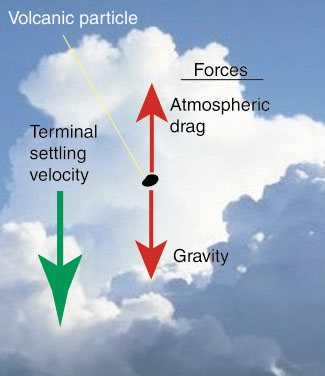
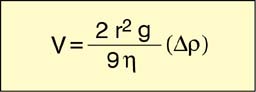 The speed at which a particle settles in the atmosphere is called the terminal settling velocity (V) and approaches a constant value as a result of the balance between the acceleration due to gravity and the atmospheric drag force.
The speed at which a particle settles in the atmosphere is called the terminal settling velocity (V) and approaches a constant value as a result of the balance between the acceleration due to gravity and the atmospheric drag force.
For simple spheres this speed can be calculated using Stokes' Law. Drag the mouse over the terms in the equation below to learn more about them.